EDITORIAL
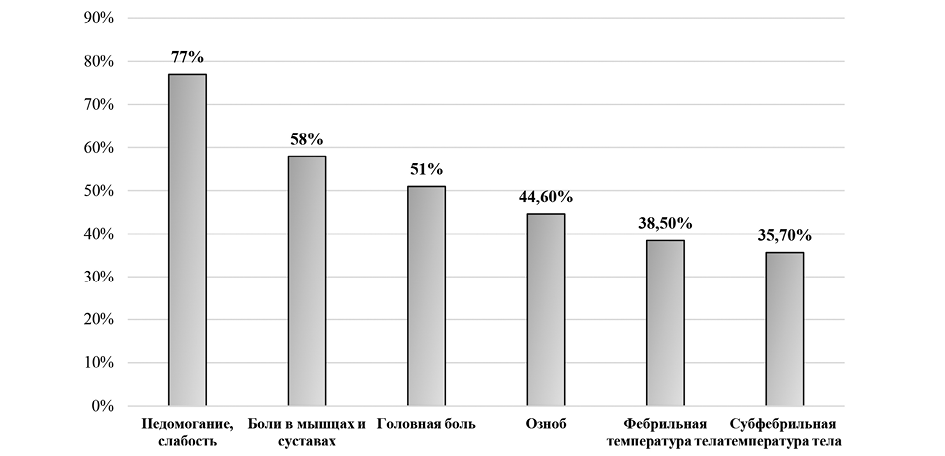
Objective: To assess the clinical, physical, and mental aspects of university students' health status following SARS-CoV-2 vaccination during the COVID-19 pandemic. Materials and methods. In 2021, an observational study was conducted in Vladivostok involving university students who had been vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2 during the COVID-19 pandemic. A total of 400 participants were enrolled: 200 students from open groups and 200 from closed groups within higher education institutions. The average age was 21.5 ± 1.5 years and 19.66 ± 1.3 years, respectively. All participants were considered conditionally healthy and had received the "Sputnik Light" vaccine. The study lasted for one month and assessed clinical, physical, and mental aspects of health following vaccination. The SF-36 questionnaire was used to evaluate quality of life. Statistical analysis was performed using Microsoft Excel and Statistica 8. Results. The analysis of the survey results using the SF-36 questionnaire showed that students from the closed educational institution who were vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2 demonstrated higher levels of physical and mental health compared to their peers from the open educational institution. Conclusion. The results of the study demonstrated a positive effect of vaccination on the physical and mental health of students, regardless of the type of educational institution. However, a comprehensive assessment of vaccine effectiveness requires an analysis of each student’s individual characteristics and their psycho-emotional background prior to vaccination. The control group, which was not vaccinated, showed decreased levels of physical and mental health, highlighting the importance of vaccination in maintaining overall health and preventing complications related to COVID-19.
REVIEWS
This article is dedicated to the problem of diagnosing locomotor function impairments in elderly people. The review presents diagnostic methods for locomotive syndrome based on questionnaire results and physical tests. A range of instrumental methods potentially suitable for diagnostics in elderly and senile individuals is identified. A critical analysis of the diagnostic value of screening questionnaires and physical examination methods is conducted. Currently, there are no universally accepted and validated diagnostic methods. Based on a literature review, it is shown that although there are various diagnostic methods for locomotive syndrome, there is a need for a comprehensive tool that can adequately account for the full spectrum of its components.
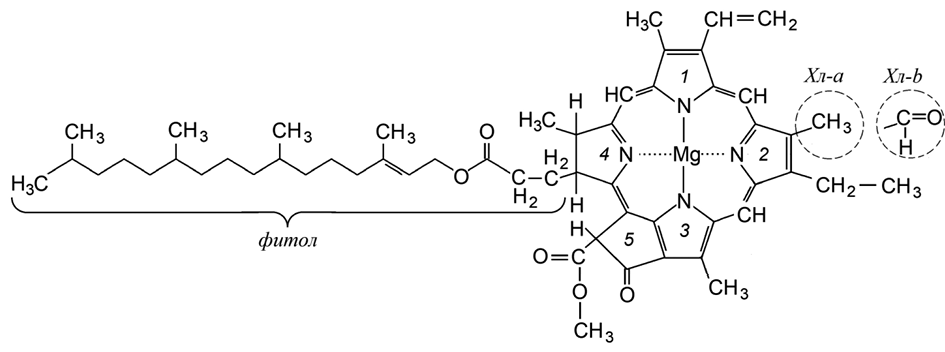
Chlorophylls are pigments of green plants with antioxidant activity that reduce the risk of chronic diseases. The review summarizes data on the therapeutic and preventive effects of chlorophylls. A chlorophyll-enriched diet demonstrates a broad spectrum of anticancer activity. Chlorophylls protect dopaminergic neurons of the brain from oxidative damage and reduce the severity of neurodegenerative disorders in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases. They also induce apoptosis in adipocytes and may serve as preventive agents against obesity. However, the metabolic pathways of chlorophylls when consumed with food and digested in the gastrointestinal tract remain insufficiently studied. Chlorophylls are relatively unstable and undergo degradation during the processing and storage of plant materials. Future research should focus on comparing the therapeutic efficacy of chlorophylls and corresponding pharmaceutical drugs under clinical conditions.
This paper reviews the evolution of approaches to the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The main treatments for liver cancer are discussed, including surgery, resection, and liver transplantation, as well as a number of non-invasive techniques, such as radiofrequency ablation (RFA) and transarterial chemoembolization. The treatment of HCC is a multidisciplinary and multifaceted task; at the same time, surgical treatment is currently the only method that can potentially cure the patient. Over the past two decades, the treatment of HCC has become remarkably more effective, mainly in the areas of both drug and surgical treatment. Over the past decades, the variety of HCC treatment methods has significantly increased and includes both traditional and minimally invasive surgical interventions, as well as targeted and immunotherapeutic approaches. RFA makes it possible to effectively and reproducibly control local tumors with minimal trauma in small HCC and metastasis, which makes RFA the preferred treatment at the early stages of HCC. Due to the potential of ultraselective chemoembolization for the treatment of small HCC, including hypovascular areas of tumor, this technique may replace surgical resection and RFA in selected HCC patients at the BCLC 0 and A stages. Unpredictable asymptomatic HCC progression at the time of initial diagnosis makes less than 30% of patients candidates for radical treatment. Systemic therapy is supposed to be an effective technique for treating patients with moderately progressive HCC. The complex HCC pathogenesis has inspired researchers to search for various biomolecular target therapies aimed at specific targets. Proper understanding of the molecular HCC mechanism presents a key to finding an effective target therapy. Significant clinical benefits in systemic therapy are observed when target drugs are combined with immunotherapy, while a sequential treatment with multiple drugs provides satisfactory survival in progressive HCC. The choice of treatment tactics should be individualized, taking into account the stage of the disease, the general condition of the patient, and comorbidities. Timely prevention, early diagnosis, comprehensive approach, and availability of new treatment methods remain important aspects
A modern comprehensive method for the treatment of periodontitis is the result of many years of laboratory and clinical research conducted in numerous countries worldwide. Until recently, its application was considered the only proven and reliable solution by treating physicians. However, the long-recognized problem of pathogenic microorganisms developing resistance to commonly used antibiotic drugs has reached truly alarming proportions over the past few years, deeply affecting many areas of medicine. This issue is especially reflected in the treatment of periodontitis, where the effective loss of key etiological therapy has significantly reduced the overall effectiveness of the treatment regimen, exacerbating previously compensated shortcomings and side effects. In this context, periodontists are compelled to seek new methods of antimicrobial and reparative therapy. In their search, attention is increasingly turning to the use of light-based physiotherapeutic treatment methods, whose therapeutic effects have long been noted but have not been adequately studied or clinically tested. The objective of this study is to examine the effects of using low-level lasers as excitation light sources in photodynamic therapy (PDT) for the treatment of patients with periodontitis. A special focus will be placed on studying the confirmed effects of light exposure from low-level lasers and the products of photochemical reactions on immune and connective tissue cells of the human body, as well as their significance in resolving pathological processes in the periodontium. The study also aims to highlight the advantages of combining this method with conventional comprehensive treatment approaches for periodontitis, addressing the shortcomings of the latter identified by modern medicine
ORIGINAL RESEARCHES
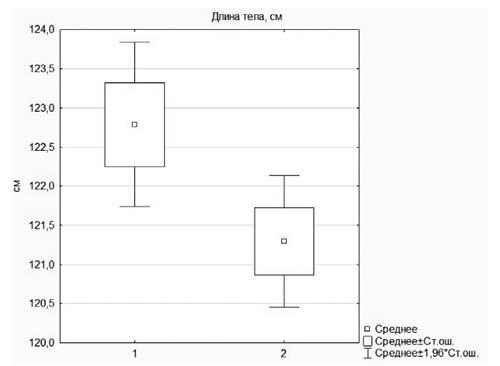
Objective: To assess the physical development indicators of contemporary preschool-aged children and identify trends in these indicators over a 25-year observation period. Materials and methods. A comparative assessment of height and weight parameters was conducted, and body mass index (BMI) was calculated for 356 six-year-old children in the 2022–2023 academic year (155 boys and 201 girls). These data were compared with physical development indicators from 290 children (138 boys and 152 girls) assessed in the 1998–1999 academic year. Physical development was considered appropriate for age and sex when the indicators fell within the 25th to 75th percentile range. Descriptive statistical methods and Student’s t-test were used; the critical significance level was set at p < 0.05. Results. Over the 25-year observation period, an increase in overall body size was observed among six-year-old children, including significant increases in body height (boys: Student’s t = 7.19, p = 0.0001; girls: t = 7.37, p = 0.0001) and body weight (boys: t = 6.79, p = 0.0001; girls: t = 8.00, p = 0.0001), as well as in mean BMI values (boys: t = 2.70, p = 0.0073; girls: t = 3.25, p = 0.0013). Conclusion. An increase in anthropometric indicators was observed among six-year-old children in the Moscow region over the 25-year period, which may reflect improvements in living conditions. The fact that BMI values fall within the "above average" range serves as a basis for implementing health education programs aimed at both children and their parents to promote BMI monitoring and control
Objective. To develop and validate a mathematical model for predicting the risk of mortality based on patients’ laboratory indicators from blood and urine tests. Materials and methods. Clinical data of patients, including laboratory test results of blood and urine, were analyzed. Mathematical modeling and statistical analysis methods were used to develop the predictive model. Results. A predictive model demonstrating high accuracy in assessing the risk of adverse outcomes was developed. The model is based on readily available laboratory indicators and can be easily integrated into clinical practice. Conclusion. The proposed mathematical model represents an effective tool for early diagnosis of mortality risk. The practical significance of the study lies in the potential application of the developed model across various fields of clinical medicine to optimize the diagnostic and therapeutic process
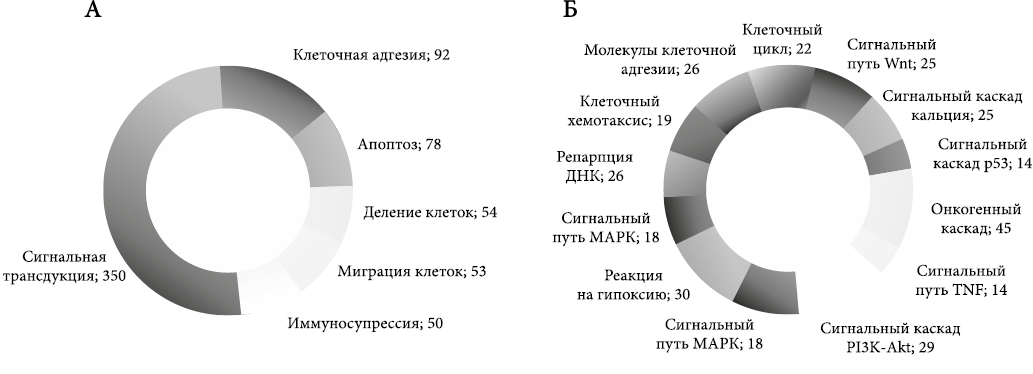
Objective. To identify pharmacological targets to enhance the effectiveness of chemoradiotherapy. Materials and methods. A highly sensitive transcriptomic analysis using high-density microarrays, routine cell technologies, and advanced bioinformatic analysis were employed. Results. A total of 677 genes were identified in CD133+ glioblastoma stem cells (GSCs) with expression levels increased by two-fold or more compared to differentiated glioblastoma cells (DGCs). Among them, 13 transcripts demonstrated a critically elevated expression in GSCs (more than 4-fold), including: akt1, hdac1, cnnb1, ahnak2, daam, pik3cg, mctp1, Il31ra, ca9, csnk2b, col6a1, col6a3 and lambd1. Conclusion. The primary pharmacological targets in glioblastoma stem cells (GSCs) are the proteins AKT1, HDAC1, and CTNNB1 – the products of the akt1, hdac1, and ctnnb1 genes. Secondary targets include the protein products of the ahnak2, daam, pik3cg, mctp1, il31ra, ca9, csnk2b, col6a1, col6a3, and lambd1 genes
Objective. To identify the spectrum of Mycobacterium tuberculosis genotypes circulating in Primorsky Krai and their significance in shaping the epidemiological situation. Materials and methods. The prevalence of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) was assessed based on monitoring data from the Primorsky Regional Tuberculosis Dispensary. To identify the genotypes of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB), DNA was extracted from patient samples obtained at the dispensary’s bacteriological laboratory in 2015–2016. Culture samples were placed in a special preservative and sent to the Laboratory of Epidemiologically and Socially Significant Infections at the Scientific Center for Family Health and Human Reproduction Problems in Irkutsk, Russian Federation, where genotyping was performed using the 24-locus MIRU-VNTR method. A total of 99 DNA samples of M. tuberculosis were used in the study. The sample included both female (38 patients) and male (61 patients) individuals, with a mean age of approximately 41 years. The majority of patients (65 individuals, 65%) were diagnosed with infiltrative tuberculosis. Statistical analysis was performed using standard methods with Microsoft Excel 2010 and Statistica 10 software. Results. The incidence of MDR-TB in the population of Primorsky Krai remains relatively stable, with no significant decrease in its transmission activity. The genotypic structure of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in the region includes six genotypes, with a marked predominance of the Beijing family (Beijing genotype – 72.7%). Strains of the CC2/148 subtype belonging to the Beijing family demonstrated a statistically significantly higher level of multidrug resistance compared to the CC1 subtype. Conclusion. The high epidemiological significance of MDR-TB and the predominance of the Beijing family strains with a high level of drug resistance highlight the need to improve epidemiological surveillance of tuberculosis in Primorsky Krai
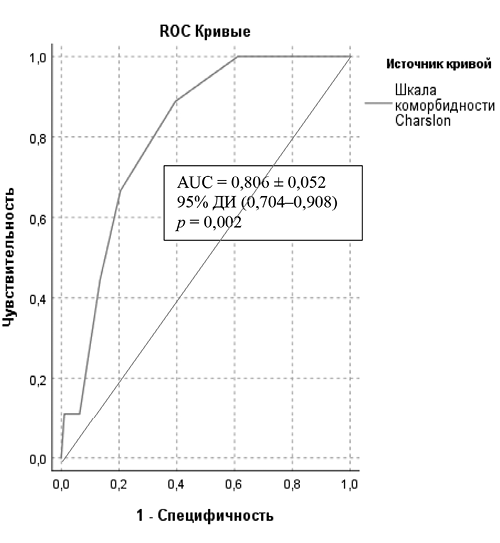
Objective. To assess the factors influencing mortality over a one-year follow-up period in outpatients with chronic heart failure and with preserved and mildly reduced left ventricular ejection fraction. Materials and methods. An open prospective controlled non-randomized study included 292 patients who were followed in the City Polyclinic No. 8, Tyumen, Russia, during 2021–2024. A total of 89 parameters were assessed, characterizing heart failure (severity of structural heart abnormalities, left ventricular ejection fraction, six-minute walk test, NT-proBNP levels and their dynamics); comorbid conditions; pharmacotherapy; vaccination status during the study period; and psycho-emotional characteristics (scores on the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale [HADS], Morisky-Green test, Type D personality assessment [DS-14], self-care ability according to the EHFScBS-9 questionnaire, and self-assessed cognitive impairment using the McNair and Kahn scale). Results. In the group of deceased patients, a higher body mass index (p = 0.034), higher Charlson comorbidity index score (p = 0.001), and higher self-care score (p = 0.015) were observed, along with a slightly lower baseline six-minute walk test result in meters (p = 0.065). A binary logistic regression prognostic model was developed based on the analysis of mortality causes during the follow-up period. For continuous variables identified as significant factors, ROC analysis was performed. Conclusion. A subgroup of patients with chronic heart failure and with preserved and mildly reduced ejection fraction was identified as having an increased risk of mortality during the one-year outpatient follow-up period. This group included patients with NYHA functional class III–IV heart failure, obesity, a Charlson comorbidity index score greater than 4, reduced self-care ability, and Type D personality
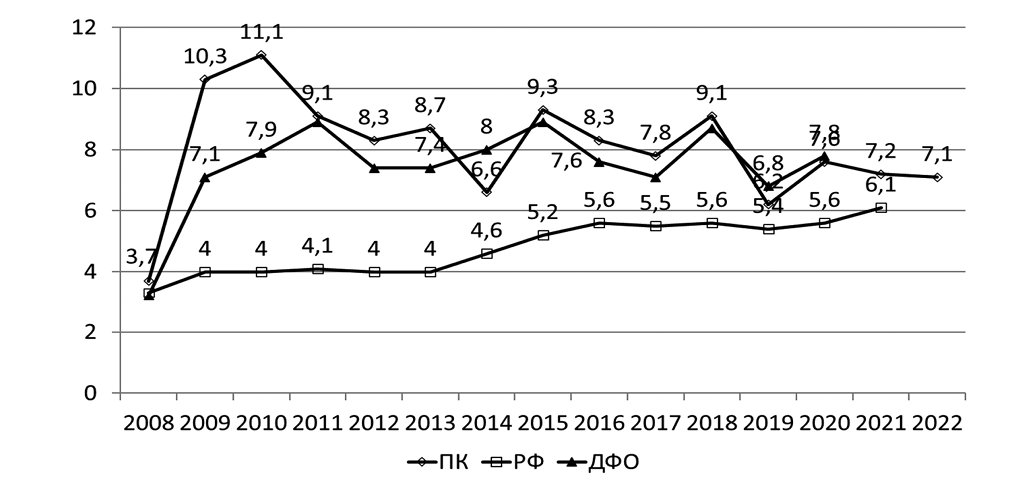
Objective: To assess the anthropometric indicators of children and adolescents with a low level of habitual physical activity. Materials and methods. A total of 640 children (306 girls and 334 boys) were examined at the following age stages: Stage 1 – preschool period at 6–7 years old, Stage 2 – school period at 8–9 years old, and Stage 3 – adolescence. The pedometry method and anthropometric measurements with index calculations were used to assess the level of physical activity; evaluations were conducted using percentile tables. Statistical analysis was performed using Microsoft Office Excel and Statistica 26.0. Results. Constitutional characteristics of anthropometric indicators were identified in the sample of children with low habitual physical activity. A trend toward an increase in excess body weight was revealed in the pediatric population: 10.7% of boys and 10.3% of girls in the older preschool group, 15.6% of boys and 13.7% of girls in the younger school-age group, and 18.6% of boys and 18.3% of girls during adolescence. The level of physical activity in these groups corresponded to the 5th–10th percentile range ("very low level"). Conclusion. The analysis revealed a significant number of children with excess body weight and low levels of physical activity. The findings underscore the necessity of assessing habitual physical activity levels alongside morphological characteristics.
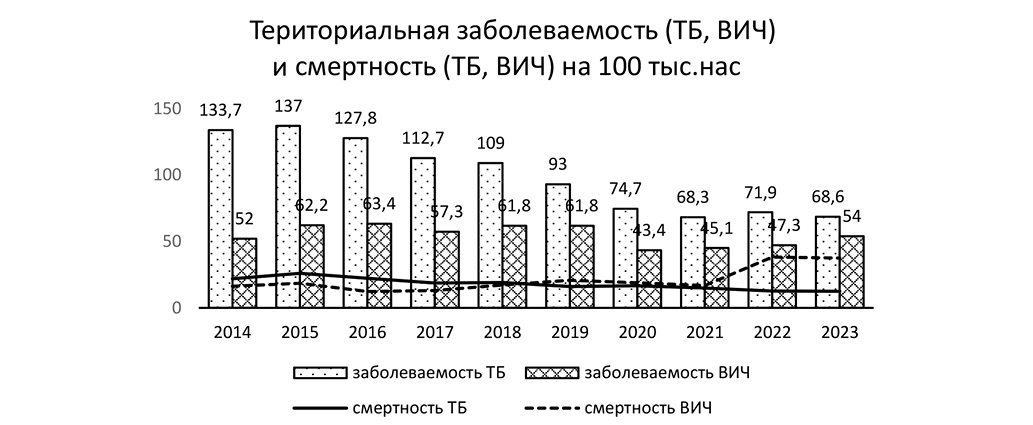
Objective: To investigate the effect of regional HIV and tuberculosis incidence on the number of adverse outcomes in a tuberculosis hospital. Material and methods. This study is retrospective and non-randomized. The analysis includes data from the Russian Federal Service for Surveillance in Healthcare (Roszdravnadzor) on the incidence, prevalence, and mortality of HIV infection and tuberculosis in the Primorsky Krai region, as well as medical records of deceased patients from the tuberculosis hospital during the period from 2014 to 2023. Results. The epidemiological situation of tuberculosis in Primorsky Krai remains unstable and tense, representing one of the leading causes of death among the HIV-positive population and significantly affecting the mortality rate of HIV-infected patients. Correlation analysis assessing the strength of the associations between regional incidence and mortality from HIV infection in the tuberculosis hospital showed no significant association (p > 0.05), which, in our opinion, indicates a lack of influence of the tuberculosis service on the processes of timely detection, early diagnosis, and treatment of HIV patients. There is a direct correlation between the increase in adverse outcomes from surgical complications and the rising number of HIV-infected patients in the tuberculosis hospital (p < 0.05); moreover, adverse outcomes among HIV patients accounted for up to 35% of all deaths. Conclusion. No observed trend toward a decrease in HIV-related mortality exists in Primorsky Krai. The majority of adverse outcomes in the tuberculosis hospital among patients with HIVassociated infections are due to insufficient geographical coverage for case detection and timely diagnosis, as well as low adherence of the patient population to tuberculosis chemoprophylaxis
PRACTICE OBSERVATIONS
The scientific article presents a clinical case involving a diagnostic search related to splenic disease. The patient underwent a comprehensive examination and consultations with various specialists. As a result, a benign nature of the lesion in the unpaired parenchymal organ was established, and a follow-up management strategy was adopted, involving observation over the course of one year, followed by re-evaluation and a final decision on further management. The article analyzes data from current domestic and international literature sources concerning splenic pathology. The authors identified key features, emphasized the complexity of diagnosing splenic diseases, and highlighted the importance of histological examination of the affected organ to ensure an accurate final diagnosis
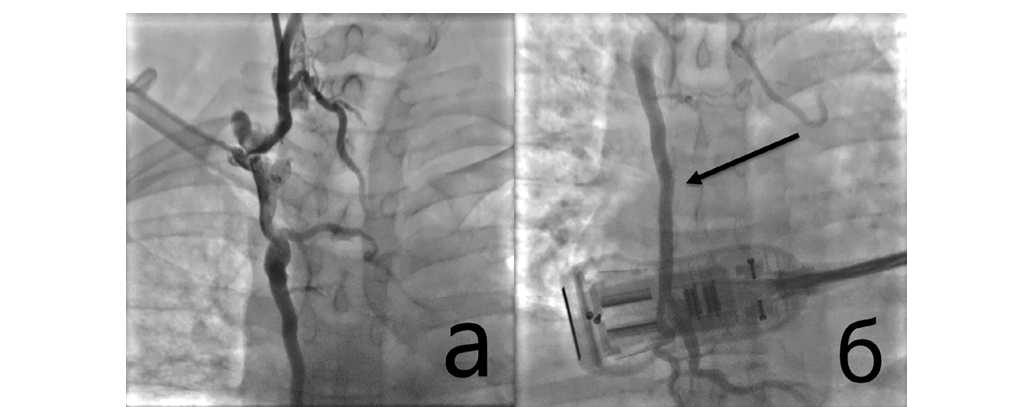
Objective. To present a clinical case of successful endovascular treatment of iatrogenic superior vena cava syndrome (SVCS) using balloon angioplasty. Materials and methods. A 37-year-old patient with a history of chronic kidney failure on renal replacement therapy was admitted with pronounced SVCS symptoms. Contrast-enhanced CT and ultrasound of the brachiocephalic veins were performed. Following an unsuccessful attempt at recanalization, balloon angioplasty was carried out in an interventional radiology suite. Results. Successful recanalization and restoration of venous outflow were achieved. Stenting was not required. The postoperative period proceeded without complications, and clinical improvement was observed. Conclusion. Balloon angioplasty can be an effective and safe treatment option for iatrogenic superior vena cava syndrome (SVCS). The minimally invasive nature of the procedure allows for significant clinical improvement even in high-risk patients
Burn disease in the stage of acute burn toxemia represents a symptom complex of interrelated and mutually aggravating pathological conditions, which can be appropriately grouped under the term "syndrome of mutual burdening". This primarily includes systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) characterized by severe endotoxemia, immunosuppression, and hypermetabolic syndrome. One of the key components of multimodal treatment for severe thermal injury is the implementation of comprehensive detoxification therapy, which makes it possible to prevent the development of burn disease complications and improves the overall prognosis. The use of hemodiafiltration procedures in patients during the burn toxemia stage leads to significant improvements in hemodynamics, pulmonary oxygenation, and correction of pathological disturbances in homeostasis. The obtained data demonstrate new possibilities in the intensive care of patients with deep burns. Incorporating hemodiafiltration into the treatment protocol may reduce mortality and shorten the duration of hospitalization
PUBLIC HEALTH ORGANIZATION
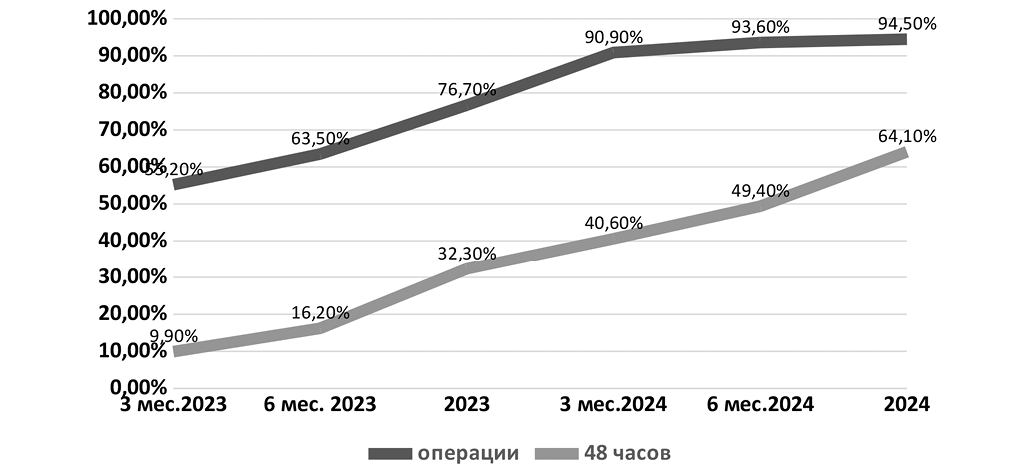
Objective: To evaluate the outcomes of implementing the algorithm from the Federal Clinical Guidelines "Proximal Femoral Fractures" into the practice of the trauma service at Vladivostok Clinical Hospital No. 2. Materials and methods. With the implementation of the clinical guidelines at Vladivostok Clinical Hospital No. 2, a local protocol for the diagnosis and treatment of patients with proximal femoral fractures was developed. During the period from 2023 to 2024, 1,345 patients with proximal femoral fractures were treated at the hospital, which accounts for 12.9% of all hospitalized patients. The entire patient cohort was classified according to ICD-10 into the following subgroups: fracture of the femoral neck (S72.0), pertrochanteric (intertrochanteric) fracture (S72.1), and subtrochanteric fracture (S72.2). Results. By the end of 2024, the overall proportion of operated patients increased to 94.5%. Mortality in the operated group decreased from 2.45% in 2023 to 2.2% in 2024. In-hospital mortality among nonoperated patients reached 17.9%. The proportion of patients who underwent surgery within the first 48 hours increased from 32.2% at the end of 2023 to 64.2% by the end of 2024. Conclusion. The implementation of clinical guidelines for the treatment of patients with proximal femoral fractures, as presented in this study and carried out at Vladivostok Clinical Hospital No. 2, highlights the identified challenges and provides a framework that can be applied in other hospital settings
PEDAGOGY
An alternative and accessible simulator model for mastering the tendon suturing technique is described. The simulator is assembled using LEGO construction elements. The support base consists of a 25.5 × 25.5 cm plate. Two holders for the "artificial tendon" are built from beams measuring 8 cm and 4 cm in length and 1.5 cm in width. Silicone tendon prostheses are used as the tendon model. The tendon model is fixed to the base. A gap is formed between the beams to hold the silicone rod under tension. The developed simulator offers advantages over existing commercial models and provides optimal conditions for junior surgeons to acquire skills in tendon repair procedures. It is also valuable for experienced surgeons for testing new suture materials, surgical instruments, tendon prostheses, and novel suturing techniques and formats