REVIEWS
The paper presents an analysis of parasitological situation with paragonimiasis in Primorsky Krai over the past 30 years. In the early 1990s regular medical checkups detected paragonimiasis in 1–6% of the inhabitants of the region. Since 1996, the situation in the south of the Russian Far East has changed dramatically. Within 1–2 years, the crayfish population decreased significantly in watercourses from southern Primorye up to the Amur basin. Therefore, the incidence of the disease in population of the region has decreased to zero level since 2000. From 2014 the number of crayfish in watercourses of Primorsky Krai started growing. In 2019 the first patient with larval paragonimiasis was reported. The paper reviews the experience of the Regional Clinical Hospital of Vladivostok in treatment of 368 patients with larval paragonimiasis for the period from 1967 to 1996. On average, the disease manifested itself in 1–4 weeks from the moment of infection. The diagnosis was confirmed in 97.9% of cases via serological method. The praziquantel treatment of patients with larval paragonimiasis resulted in a cure rate of 89%. The disease duration ranged from 1–2 to 10 or more years.
The introduction of modern robot-assisted and laparoscopic methods of surgical interventions have extended the range of surgical indications, at the same time as raising a number of specific problems related to the technical features of minimally invasive treatment. This fact makes us consider the effect of surgical aggression on the patient from a new perspective. In particular, the influence of pneumoperitoneum and the patient’s position on venous return, regional blood flow changes, and concomitant shifts of some homeokinetic systems require elucidation. This article reviews the available literature to describe the main features of anesthesia during robot-assisted surgical interventions. Recommendations from systematic reviews and meta-analyses were used. The search depth comprised the period of 12 years (2011–2022). Such factors as antiphysiological position on the operating table, tense carboxyperitoneum, and carboxythorax affect almost all organs and many regulatory mechanisms, thus having a pathological effect on the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, kidney, liver, intestines, blood coagulation system, immune system, and thermoregulation mechanisms. These effects are particularly pronounced in patients with concomitant diseases. In addition to knowledge in the field of pathophysiology, surgeons should be capable of predicting the course of events to take actions aimed at preventing the development of complications. Robot-assisted surgical interventions, although being less traumatic, are characterized by specific features that should be taken into account when preparing a patient to undergo surgery, selecting an optimal method of surgical intervention, and managing the patient in the intra- and postoperative period with rehabilitation.
Literature review involves a problem analysis of current scientific publications on yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida of the family Saccharomycetaceae. In 90% of cases, the etiological factor of chronic, recurrent infectious and inflammatory processes is represented by residents of oral, intestinal, urogenital and skin microbiome, opportunistic Candida albicans fungi. The paper considers the relevant medical and social problem of endogenous opportunistic infections on the example of candidiasis (candidamycosis). The review presents a conceptual analysis of changes in the microbiological properties of clinically significant candida species with ubiquitous distribution: Candida albicans, Candida tropicalis, Candida glabrata, Candida krusei, Candida parapsilosis, Candida dubliniensis, Candida auris. The authors provide a current perspective on the risk of superficial and invasive candidomycosis as an opportunistic, non-cyclic infection. Signs of the same type of pathological process develop with the participation of different species of opportunistic fungi in monoculture and associations against the background of immunodeficiency.
This review article is devoted to ultrasound monitoring of intravascular volume status and organ perfusion in critically ill patients. In particular, approaches to determination of fluid responsiveness using Doppler-estimated blood flow in peripheral arteries are discussed. The reliability and accuracy of these parameters are substantiated by their comparison with the parameters obtained by prepulmonary and transpulmonary thermodilution methods. The technicalities of ultrasound examination of the abovementioned parameters are considered.
ORIGINAL RESEARCHES
Aim. To investigate the potential for searching new virulent bacteriophages in the paleontological material extracted from the permafrost zone.
Material and methods. The virome structure of the colon content of the wolf pup mummy (Canis lupus) from the late Pleistocene was evaluated by means of shotgun metagenomic sequencing.
Results. The study demonstrated the predominance of Myoviridae tailed bacteriophages, including PhiKZ-like phages, in the structure of the virome.
Conclusion. The results of the study indicate the possibility of using paleontological material preserved in the ancient Arctic permafrost as a resource for searching and isolating new virulent bacteriophages.
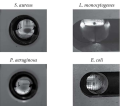
Objective. To evaluate the potential of magnetic levitation systems when studying the autoaggregation of gram-negative and gram-positive pathogenic bacteria and elucidating mechanisms controlling autoaggregation.
Materials and methods. Escherichia coli O157:H7, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, and Listeria monocytogenes were used. The number of alive bacteria was determined using a Live/Dead® dye. E. coli curli were stained with Congo red.
Results. All four tested bacterial species formed autoaggregates that levitated within the liquid volume for up to 72 hours (observation time). After 72 hours, the number of alive bacteria in the autoaggregates ranged from 82% (E. coli) to 99% (L. monocytogenes). The formation of E. coli autoaggregates was shown to depend on the production of curli, which represent surface structures playing an important role in biofilm formation.
Conclusion. The proposed system of magnetic levitation can be used to study molecular mechanisms of bacterial autoaggregation and flocculation.
Aim. To investigate the relationship of SNP ACE ((AluIns/DelI>D), rs 4646994), SNP of angiotensinogen 1 gene AGT :521 C>T ((Thr 174 Met), rs 4762), SNP of angiotensinogen 2 gene AGT:704 T>C ((Met 235 Thr), rs699), SNP of angiotensin-2 type 1 receptor gene AGTR1: A1166C; A>C (rs5186) with left ventricular diastolic dysfunction in hypertensive patients.
Methods and materials. 74 patients (26 women and 48 men) with stage 1-2 hypertension were examined. The analysis of genetic polymorphisms was carried out by means of polymerase chain reaction method with the analysis of DNA RFLP (restriction fragment length polymorphism).
Results. CC polymorphisms of genotype AGT:704 T>C (Met 235 Thr), (χ2 = 8.18; p = 0.017) were detected in the group of patients with left ventricular diastolic dysfunction, which nearly triples the probability of impaired myocardial relaxation (OR 2.85) and CC polymorphisms of genotype of angiotensinogen type 1 receptor gene (AGTR1: A1166C), (χ2 = 1.77; p = 0.041), which doubles the probability of left ventricular diastolic dysfunction (OR 2.39).
Conclusion. CC genotype AGT:704 T>C (Met 235 Thr) and CC genotype of the angiotensinogen type 1 receptor gene (AGTR1: A1166C) are associated with the development of left ventricular diastolic dysfunction in patients with hypertension.
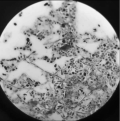
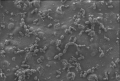
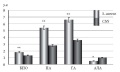
Aim. To assess the intensity and characteristics of bacterial biofilms formed by non-fermenting gram-negative bacteria Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii on ceramic biocomposite samples based on wollastonite and zirconia, including those modified with the bioactive phase of hydroxyapatite (HA).
Materials and methods. Biofilms formed on bioceramic samples, prepared according to the author’s original method, were examined by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The studied samples included non-composite ceramics based on wollastonite (CaSiO3); composite ceramics based on wollastonite with HA (CaSiO3-HA); non-composite ceramics based on zirconium dioxide ZrO2; ceramics based on zirconia with HA 15 wt% (ZrO2-(15 wt % HA); ceramics based on zirconia with (ZrO2-(50 wt% HA). Biofilms were obtained by placing the samples in a nutrient medium with P. aeruginosa and A. baumannii. Cultivation was carried out at 37 °С for 24 and 48 h, respectively. The dynamics of bacterial growth of the surface of the studied samples was assessed by analyzing SEM images using an LBP classifier.
Results. A noticeable difference was observed in the activity and structure of bacterial biofilm formation on all studied samples. The intensity of biofilm formation (surface coverage of ZrO2-based samples) determined using an LBP-based classifier was as follows: ZrO2 ceramics without HA – 28.13%; ZrO2 + 15 wt% HA – 28.33%; and ZrO2 + 50 wt% HA – 88.46%. All samples with HA addition demonstrated higher susceptibility to biofilm formation.
Conclusion. The presence of HA in the composition of bioceramics increases the intensity of biofilm formation. This also indicates a higher biocompatibility of such materials. When selecting bioceramic materials for bone defect repair, preference should be given to materials containing no more than 15 wt% HA in the view of reducing the risk of infection.
Aim. To evaluate the feasibility of an accelerated method for determining the etiology of infections in urine, dialysate and residual antimicrobial activity by using laser light scattering technology.
Materials and methods. From January to September 2019, 106 urine samples and 42 dialysate samples from children aged 1–16 with various urinary pathologies and those on peritoneal dialysis underwent culture-based examination on an ALIFAX HB&L LIGHT analyzer (Alifax, Italy) using laser light scattering technology.
Results. Three hours after inoculation, 81 samples (76.4%) appeared to be negative and 25 samples (23.6%) proved to be positive. No microorganisms were detected in 38 dialysate samples (90.5%), two samples had Staphylococcus aureus (104 CFU/ml), and one dialysate sample had Corynebacterium sp. and associations of Escherichia coli + Candida albicans + Staphylococcus haemolyticus, associated with peritoneal catheter colonization. Bacteriuria was caused by Enterobacterales in 39.3% (E. coli, Morganella morganii, Citrobacter amalonaticus, Enterobacter cloacae), non-fermenting gram-negative bacteria – in 14.3% (Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Ralstonia picketii, Oligella sp., Acinetobacter baumannii), Enterococcus sp. – 21.4%, S. haemolyticus, Staphylococcus epidermidis – 10.7%, Candida albicans – 3.6%, contamination: Streptococcus viridians, Corynebacterium sp. – 7.1%. Residual antimicrobial activity in urine was detected in 30.1% of patients.
Conclusion. The laser light scattering technology enables a minimal concentration of microorganisms to be detected in a smaller amount of urine or dialysate, which is very important for accelerated diagnosis of urinary tract infections and complications of peritoneal dialysis in children.
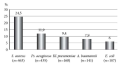
Objective. To investigate the susceptibility of K. pneumoniae and P. aeruginosa to a polyvalent bacteriophage preparation and its effect on biofilm formation and the strain biofilms isolated from orthopedic patients.
Materials and methods. The research sample included 50 clinical isolates of K. pneumoniae and 50 clinical isolates of P. aeruginosa. Identification was performed by MALDI-TOF-MS; antibiotic susceptibility was assessed in accordance with EUCAST v 21. Detection of carbapenemase genes was carried out by real-time PCR. The strain susceptibility to the bacteriophage was determined by a spot test; K. pneumoniae ATCC 33495 and P. aeruginosa ATCC 27853 were determined by assessing their growth curves. Biofilms of strains sensitive to bacteriophages were formed according to the O’Toole method by co-incubation of bacteria with phages. The effect of bacteriophages on 24-hour biofilms was assessed by comparing the optical density of dye extracts of bacteriophage-treated wells and control wells at 570 nm. The data were analyzed using the Statistica environment.
Results. It was found that 7 (14%) of K. pneumoniae and 15 (30%) of P. aeruginosa were resistant to carbapenems. Six strains of K. pneumoniae produced NDM-cabapenemase, while four isolates of P. aeruginosa produced VIM-carbapenemases. The bacteriophage preparation under study was active against 36% and 56% of K. pneumoniae and P. aeruginosa strains, respectively. The majority of the studied strains reduced biofilm production upon co-incubation with a phage; however, a decrease in biomass of greater than 80% was observed only for P. aeruginosa. The effect of the bacteriophage on the already formed biofilms was less pronounced, despite a decrease in the biofilm biomass in 78% and 68% of K.pneumoniae and P. aeruginosa strains, respectively.
Conclusion. The results obtained confirm the need for further research into the action of bacteriophages against pathogens caused by implant-associated infections and the development of bacteriophage therapy for orthopedic patients.
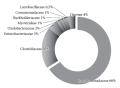
Aim. To evaluate clinical significance of simultaneous vegetation by conducting microbiological research of the species composition in the periodontal pockets and on the surface of the tongue root and back in chronic (generalized) periodontitis.
Materials and methods. A prospective microbiological analysis of clinically significant species of opportunistic microorganisms in pathological periodontal pockets and the microbiome of the tongue root and back, in chronic (generalized) periodontitis of mild, moderate and severe degree, was carried out in 88 patients of the WHO key group, aged 35–44 (CI 95% 34.8–44.3), of the Unistom Dental Clinic of the Far Eastern State Medical University, Khabarovsk Krai, for the period 2016–2019.
Results. The species composition of opportunistic microorganisms in the biotopes of the pathological periodontal pockets and tongue root and back was the same in chronic periodontitis, with a mean value of 89.7% ±2.9% (CI 95% 85.8–94.4). The mean value of the number of species of clinically significant opportunistic microorganisms in the periodontal pockets and root and back of the tongue in associations accounted for 3.9 (CI 95% 1.8–5.4). Bacteria of the genus Leptotrichia were detected simultaneously in periodontal pockets and on the root and back of the tongue in clinically significant associations with Staphylococcus aureus (CI 95% 37.3–65.4), mean Shannon index H value 3.1 ± 0.4; mean Simpson index C value 0.39 ± 0. Bacteria of the genus Leptotrichia in association with Streptococcus pyogenes (CI 95% 35.8–79.3), mean Shannon index H 2.9 ± 0.3; mean value of the Simpson index C 0.28 ± 0.06, reliably support the recurrent course of the opportunistic infectious and inflammatory process in the periodontium. The dominant role of Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes in the biotopes of periodontal pockets and the root and back of the tongue in exacerbations of chronic periodontitis has been established. Titre of opportunistic microorganisms in pathological periodontal pockets of 2–5lgCFU (colony-forming units) in mild and moderate degree of severity is 1–2 order lower than titre of opportunistic microorganisms in root and back of the tongue of 4–6lgCFU (95% CI 2.1–6.5).
Conclusions. Evaluation of simultaneous vegetation of opportunistic microorganisms in the oral microbiome provides a means for improving laboratory (microbiological) diagnostics in chronic periodontitis and applying a non-invasive microbiological method for indirect diagnosis of the species composition of opportunistic microorganisms in periodontal pockets according to the composition of opportunistic microorganisms of the root and back of the tongue in chronic periodontitis for prophylaxis and treatment personalization.
Objective. To characterize pathogenic pheno- and genoprofiles of staphylococci of different species, isolated from the secretion of the prostate gland in male patients with chronic bacterial prostatitis.
Materials and methods. The bacterial spectrum of microflora was studied by a bacteriological method; the species identification of microorganisms was carried out by mass spectrometry. Detection of genes determining pathogenicity factors was carried out by PCR. The biofilm-forming ability of staphylococci, as well as their anti-lysozyme, hemolytic, and adhesive activity, were determined by photometry.
Results. Staphylococci were found to be dominant in the pathogen structure of chronic bacterial prostatitis. These microorganisms, regardless of their species, had a pronounced pathogenic potential. Specific features in the bioprofiles of cultures of different species were determined according to the severity of the studied biological properties. Thus, the hemolytic activity and biofilm-forming ability was significantly higher in S. aureus. Conversely, CNS strains were characterized by high anti-lysozyme activity. A significant difference was noted in the prevalence of genes that determine pathogenicity factors in the studied staphylococci of different species.
Conclusion. The pathogenic bioprofile of staphylococci of various species isolated from patients with chronic bacterial prostatitis can be used as a criterion in the search and identification of the pathogen, as well as in the development of effective therapeutical approaches.
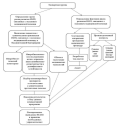
Aim. To conduct comprehensive evaluation of microbiological properties of Enterococcus faecalis, isolated from urine in children with urinary system infections (UTI), to determine their etiological significance.
Materials and methods. The study employed clinical isolates E. faecalis (n = 51) from the urine of children aged 3 days to 17 years who were treated for urinary tract infection between 2013 and 2017. The biological properties of enterococci were evaluated by means of classical microbiological and up-to-date molecular genetic methods. Statistical processing of digital data was carried out using non-parametric methods.
Results. Phenotypic and genetic heterogeneity of microbiological properties of the studied urinary enterococci isolates was revealed. Using statistical methods of analysis, the authors established significant correlations between pathogenicity genes, antibiotic resistance and phenotypic manifestations of biological properties in urinary isolates E. faecalis. The results of evaluating the phenotypic manifestations of biological properties and the presence of certain genes enabled the enterococci to be classified into groups that correlated with certain sequence types (ST). Based on the revealed relationships of some biological properties of urinary isolates E. faecalis with certain sequence types, the authors developed an algorithm for assessing etiologically significant and highly virulent E. faecalis isolated from the urine of children with UTI.
Conclusions. A comprehensive determination of some, potentially relevant biological properties, of the pathogen – enzymatic activity associated with pathogenicity and biochemical activities, antibiotic resistance (not only at the phenotypic, but also at the genetic level) – allows for assessing the diagnostic value of urostams E. faecalis, isolated from the urine of children with UTI, which will contribute to a personalized approach to treatment of these patients.
Aim. To explore the etiological structure of wound microflora and its antimicrobial susceptibility in burn patients treated in hospital burn departments.
Materials and methods. The authors analyzed the microbiology testing results of 2354 wound exudates in samples of 1581 patients with severe burns who underwent treatment in the Burn Unit and Department of Anesthesiology, Resuscitation and Intensive Care of the Center for Emergency Medical Care of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) in the period from 2016 to 2020. Data processing and antibiotic resistance analysis were performed via AMRcloud online platform (Beta version, 05.07.2022).
Results. Of the pathogens isolated in the burn wounds, Staphylococcus aureus accounted for 26.1%, Enterococcus faecalis – 24.5%, Pseudomonas aeruginosa – 11.9%, Klebsiella pneumonia – 9.4%, Acinetobacter baumannii – 7.9% and Escherichia coli – 6.0%. The susceptibility of isolated microbial strains to carbapenems and high resistance to cephalosporins and fluoroquinolones were established.
Conclusion. Microbial strains detected in burn patients indicate infection of wounds with representatives of nosocomial flora and their high resistance to commonly used antibiotics.
Aim. To identify the difference in the detection of yeasts of the genus Candida and their species composition in people with gastrointestinal pathology and in healthy people undergoing a regular medical checkup.
Materials and methods. Clinical trial material comprised biological material from patients undergoing regular medical checkup (control group) and patients with intestinal pathology. Following the detection of fungal colonies on Sabouraud medium, identification was carried out using chromogenic agar. A number of strains were identified via mass spectrometry.
Results. The study results show that the frequency of occurrence of the genus Candida is more than three times higher in patients with intestinal pathology. In addition, the study groups revealed the differences in the species composition. Candida krusei is more than 5 times more common in cases of gastrointestinal pathology.
Conclusion. Due to the differences in the frequency and species composition of yeasts of the genus Candida isolated from the intestine, specialists should diagnose intestinal diseases and choose antimycotic therapy in a meticulous way.
Aim. To explore the relationship of physical development and nutrition pattern in primary school-aged children.
Materials and methods. 266 children have been examined for three years by means of the continuous sampling method. In order to study nutrition patterns, the questionnaire method was applied to the parents. Physical development was evaluated according to main anthropometric indicators with the identification of somatotype and degree of harmonious development. Morbidity was studied by extracting data from individual development histories.
Results. The nutrition of primary schoolers is marked by a prevalence of carbohydrates, while the amount of protein and calcium-containing products is insufficient. The physical development is disharmonious in most cases, due to underweight (82% of children) and excess weight (8%). 24% of children have a postural abnormality, 15% – caries, 3% – endemic goiter, 45% suffer acute respiratory infections more than 4 times a year.
Conclusions. Nutrition patterns in primary school-aged children are characterized by unbalanced diet, which contributes to disharmonious development and decreases stamina.
Aim. To study the indicators of quality of life (QoL) and health-related quality of life (HRQoL) among medical university students.
Materials and methods. In total, 114 people aged 18 to 23 years were included in the study. The participants were divided into two groups. Group 1 consisted of 55 medical students (MS) of the Pacific State Medical University undergoing practical training in the city of Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk (Vladivostok, Russia). In this group, male and female respondents accounted for 41.8% (23) and 58.2% (32), respectively. Group 2 included 59 students of non-medical education (NMS) from the Sakhalin State University (Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk, Russia), with 49.28% (29) male and 50.8% (30) female respondents. The effect of socio-economic factors on HRQoL indicators was determined, along with the main predictors in their decrease.
Results. In the structure of diseases defining the 2nd and 3A health groups, diseases of class IX prevailed. Diseases of the circulatory system (I00-I99) were detected in 12% and 24.4% of MS and NMS, respectively. The diseases of class XI were ranked second. Thus, digestive diseases (K00-K93) accounted for 47.8%, and ophthalmic diseases (H00-H59) accounted for 35.5%. A significant physical dysfunction was identified in more than 3% of respondents; 99% of respondents reported a decrease in working capacity. Among MS, 1.7% of respondents demonstrated signs of depression and suffered from pain of varying intensity (44.5%). A decreased social activity was observed in 4% of NMS respondents.
Conclusion. The data of QoL monitoring can be used for developing a multi-level scoring system for preventing health disorders among university students. Proposals were made concerning healthy lifestyle management. The model of dynamic monitoring of the health of university students exposed to various risk factors was supplemented. An individual route for rehabilitation and disease prevention for university students was developed based on the study of QoL.
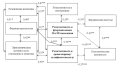
Aim. To develop an algorithm for a comprehensive assessment of endogenous and exogenous factors and risks of urinary tract infections (UTI) to improve prevention measures in multidisciplinary healthcare organizations.
Materials and methods. All patients included in the study were divided into two groups. Group 1 was formed on the basis of the Altai Regional Hospital for War Veterans (700 medical histories). Regional Clinical Hospital provided 500 medical histories. Endogenous and exogenous risk factors were assessed in patients included in the study.
Results. Following a comprehensive assessment of exogenous and endogenous risk factors of healthcare-associated UTI among patients of different ages, an algorithm for improving prevention measures has been developed.
Conclusions. The algorithm of prevention measures for expert evaluation of risk factors and groups of healthcare-associated UTI enables the prevention of these infections to be improved. The creation of databases of risk factors that contribute to infection is essential for providing expert evaluation of standard operating procedures and internal quality audits of medical activities, as well as for determining the optimal prevention measures reducing the incidence of UTIs.