REVIEWS
Arterial hypertension (AH) is one of the most common cardiovascular complications of anticancer drug therapy. In this review article, we consider the main groups of anticancer drugs that may cause the development of iatrogenic AH, the pathophysiological mechanisms of increased blood pressure, as well as the clinical significance of AH developed during treatment with cytostatics and targeted drugs in the practice of an oncologist and a cardiologist. It was found that AH is frequently associated with the use of angiogenesis inhibitors, as well as alkylating cytostatics, antimetabolites, taxanes, and proteasome inhibitors. In addition, erythropoietins, glucocorticosteroids, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs used as part of supportive therapy may contribute to an increase in blood pressure. Management of hypertension in cancer patients is an important part of antitumor treatment therapy whose implementation contributes to improving their quality of life. Research into various clinical and pathophysiological aspects of cardiovascular disorders in cancer patients is becoming increasingly relevant, which is indicated by the rapid development of cardio-oncology, a new interdisciplinary field of knowledge aimed at developing practical recommendations for the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of cardiovascular toxicity caused by anticancer therapy.
Ovarian cancer (OC) remains to be a leading cause of mortality among oncogynaecological patients. The low five-year survival rate of OC patients is associated with a lack of highly sensitive screening, early diagnostics and preventive methods, as well as high metastasis, recurrence and chemoresistance rates. Molecular genetic techniques for OC diagnosis based on standardized genetic panels can be used to detect a limited range of mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes. However, the spectrum of genes potentially responsible for OC development is much wider. Recent data emphasize the importance of personalized approaches to account for ethno-population specifics in molecular genetic testing. This paper reviews recent data on the pathogenesis, molecular genetic diagnostic methods, and preventive strategies for OC.
In this article, we consider the problem of euthanasia as a form of realization of the human right to die. The historical aspects of euthanasia are discussed along with its legal aspects. Thus, modern Russian legislation bans implementation of euthanasia by medical workers under the threat of criminal punishment. An analysis of government policies on human euthanasia was conducted, including in countries where this procedure is legalized. The results show that euthanasia is applied within strict limits, in accordance with the established order. Euthanasia was found to have no effect on mortality and suicide tendencies. In addition, the authors propose an approach to the multi-stage practical implementation of euthanasia, which is carried out by independent and disinterested specialists. At each stage, a large number of interrelated procedures is performed, each of which confirms the validity of the previous step. The patient must make a voluntary euthanasia decision based on comprehensive information about his or her health. In turn, the government should provide an alternative to euthanasia in the form of palliative care. In conclusion, the need to enshrine the principles, conditions, and mechanisms of euthanasia in Russian legislation is substantiated, which would ensure the human right to die with dignity.
ORIGINAL RESEARCHES
Aim. Selection and combination of immunodiagnostic tests to detect active tuberculosis (TB) in children with concomitant bronchopulmonary pathologies.
Materials and methods. A prospective study of children and adolescents (n = 236) was conducted, which included cases with localized pulmonary tuberculosis; pulmonary tuberculosis associated with allergic or infectious and inflammatory forms of chronic nonspecific lung diseases (CNSLD); chronic nonspecific lung diseases under a significant absence of active TB but the presence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. All patients underwent immunodiagnostic tests by Mantoux test, recombinant tuberculosis allergen (RTA) test, and QuantiFERON – GIT.
Results. Mantoux and RTA tests were found to exhibit high sensitivity in children both with tuberculosis associated with concomitant pathologies and without such pathologies. Differences were observed in the results obtained by the Mantoux test in children with tuberculosis-associated bronchopulmonary pathology and those with localized tuberculosis. The Mantoux test may be positive as a result of many factors, other than active TB infection. Thus, children with allergic and infectious-inflammatory pathologies of the lungs exhibit an altered sensitivity to the Mantoux test. Such cases require in vitro diagnostics with the Quanti- FERON test, whose sensitivity is high despite the presence of CNSLD.
Conclusions. Children with infectious-inflammatory CNSLD should undergo TB examination in stages based on in vivo and in vitro tests, when necessary. Children with allergic CNSLD should undergo in vitro tests at the first stage.
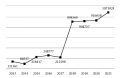
Aim. To analyze the epidemic situation of tuberculosis (TB) in the Far Eastern Federal District of Russia in the context of implementation of a targeted governmental program “Prevention and control of socially significant infectious diseases.”
Materials and methods. Performance indicators were calculated based on the information derived from official statistical forms. Conventional calculation methods were used.
Results. The incidence of TB in the Far Eastern Federal District amounted to 51.0 per 100 thousand population under the target value of 41.0. The coverage of population with preventive TB screening comprised 72.9% under the target value of 72.5% (achieved). The mortality rate in tuberculosis patients was 9.1 per 100 thousand population under the target value of 6.0. The maximum mortality rates were recorded in the Amur Oblast (15.8) and Primorsky Krai (15.3) with 55.6% of fatal cases. The share of newly-diagnosed TB cases in prisons comprised 7.7% under the target value of 7.6%. The share of newly-diagnosed pulmonary TB cases with a culture-positive result was 56.5%, which exceeded the target value of 55.5%. However, this indicator was extremely low in the Chukotka Autonomous Okrug (26.9%), Zabaykalsky Krai (29.7%), and Jewish Autonomous Oblast (31.9%). The indicator “Effectiveness of the treatment of patients with multidrug-resistant tuberculosis” was 55.9% under the target value of 57.5%. The main problem of achieving this indicator was associated with insufficient adherence of patients to treatment.
Conclusions. Tuberculosis remains to be a serious problem in the Far Eastern Federal District of Russia. Only two out of six indicators of the targeted governmental program were achieved. The epidemic situation in the Primorsky Krai and Amur Oblast requires increased attention due to their significant role in the Far Eastern Federal District as a whole. Efforts should be aimed at improving laboratory diagnostics of TB and developing programs of psychosocial support for TB patients.
Aim. To study the indicators and regional specifics of morbidity associated with temporary disability in the Subjects of the Far Eastern Federal District (FEFD) of Russia.
Materials and methods. A descriptive epidemiological study was performed based on retrospective data on the morbidity associated with temporary disability of the working population in FEFD as of January 01, 2021. A unified inter-agency information and statistical system was used to study the indicators of temporary disability (TD), including the number of TD cases per 100 employees and the number of TD days per 100 employees during 2005–2020. The methods of descriptive statistics were applied to differentially calculate the average annual indicators for the periods of 2005–2014 and 2015–2019 due to the adoption of the Rosstat order No. 723 dated December 25, 2014.
Results. The average long-term value of the indicators of morbidity associated with temporary disability in most FEFD subjects was found to be statistically significantly higher than that in the entire Russian Federation, with higher values o bserved in 2005–2014 compared to 2015–2019. The indicators of morbidity associated with temporary disability demonstrated a more stable trend during 2015–2019. The indicators for 2020 were statistically higher than for 2015–2019, largely due to the COVID-19 pandemics.
Conclusions. In view of the specific nature of the main economic sectors in FEFD (shift and seasonal work), as well as the lack of a developed social, road transport, and engineering infrastructure, data on temporary disability of the working population (including migrants) should be continuously monitored. The results obtained at this research stage can be used to develop optimal measures aimed at protecting the health of people living in the Far East of Russia.
Aim. To assess changes in the epidemic indicators of tuberculosis infection (TB) in children in the Northwestern Federal District of Russia before and after the COVID-19 pandemic based on mathematical modeling and forecasting.
Materials and methods. The main epidemiological indicators of TB were analyzed using the official statistical data for 2009–2021. A mathematical forecasting of epidemiological indicators was performed based on chest X-ray screening for TB. A statistical analysis was carried out using the software environment R (v.3.5.1) and the commercial software Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS Statistics for Windows, version 24.0, IBM Corp., 2016). Time series forecasting was performed using the programming language of statistical calculations R, version 4.1.2 and the bsts package, version 0.9.8.
Results. The mean regression coefficient of a single predictor was found to differ in a model for TB morbidity in children is 0.0098. X-ray screening for TB was established to be a significant mortality predictor in children. At least 60% of the population should undergo TB screening in order for TB prevalence to be controlled in a country with a population above 140 million people.
Conclusions. The conducted study revealed a positive correlation between the incidence of tuberculosis in children in Russia and TB screening in at least 60% of the population. Under the current TB screening system in Russia, the epidemic TB situation will continue to improve, despite COVID-19 restrictions. At the same time, in the Northwestern Federal District of Russia, preventive TB screening can be considered sufficient only in the Kaliningrad, Murmansk, and Pskov Oblasts.
Objective. To evaluate the efficacy of immunological tests for early detection of tuberculosis infection in children in the Yaroslavl Oblast (Russia).
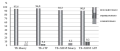
Material and methods. Medical records of 354 children and adolescents examined by ELISPOT (Enzyme-Linked ImmunoSpot) assay (T-SPOT.TB) in the Yaroslavl Oblast in 2020–2022 were studied. Four groups of children were distinguished: group 1 included children with active tuberculosis (n = 3); group 2 included children under 7 with altered tuberculin sensitivity (conversion of the tuberculin test) or children over 8 first-time tested positive for RTA, who were under the supervision of a phthisiatrician in the VI A group of dispensary registration (n = 52); group 3 included children with medical exemptions from screening immunodiagnostics (n = 49); and group 4 included children with refusals of their parents or legal representatives from skin tests (n = 250).
Results. The sensitivity of both RTA and T-SPOT.TB tests achieved 100%, with the concordance level of 100%. When assessing discordant results (positive result for RTA and negative for T-SPOT.TB) in the VI A dispensary registration group, the majority of children were found to have an aggravated allergic anamnesis and somatic pathology. The maximum number of children examined by the laboratory method included those whose parents or legal representatives refused from skin test administration (70.6%).
Conclusions. T-SPOT.TB is an optimal method for early detection of latent TB infection and TB in children at risk, including those with medical contraindications for skin tests or whose parents refused from screening immunodiagnostics.
Aim. Quantitative assessment of TREC and KREC in infants and preschool children infected with tuberculosis infection (TI).
Material and methods. A prospective cross-sectional study was conducted in 2022. The observation group consisted of 87 children of early childhood age in contact with TB patients, of whom 27 were diagnosed with TB, 34 were tested positive to TB based on skin tests without signs of a local specific process (TI), 26 were children without signs of tuberculosis infection according to the results of skin tests and local process (conditionally healthy children).
Results. The following factors significant in the assessment of tuberculosis infection were determined: anti-tuberculosis therapy (F = 42.001; p = 0.000001); positive or negative response to the tuberculosis recombinant allergen (RTA) during an intradermal test (F = 39.394; p = 0.000001); high TREC levels in the blood (F = 12.707; p = 0.000001); the presence of a tuberculin response (F = 10.625; p = 0.000006); and KREC levels (F = 3.182; p = 0.039).
Conclusions. According to the obtained results, TREC levels can be considered as a personalized risk predictor of tuberculosis infection in infants and preschool children.
Objective. To carry out a screening study among children and adolescents for tuberculosis infection in the city of Moscow using modern immunodiagnostic methods.
Materials and methods. The results of a mass screening study for tuberculosis prevalence in the pediatric population of a metropolis city were analyzed. The study was conducted during 2019–2021 in Moscow using the Mantoux skin test with 2 TE PPD-L and a skin test with a recombinant tuberculosis allergen (RTA), as well as the indicators of tuberculosis incidence in children.
Results. The introduction of mass screening for tuberculosis based on RTA among the pediatric population and subsequent work with the identified risk groups contributed to a decrease in the number of newly-diagnosed cases. In 2019–2021, the incidence of tuberculosis among children in Moscow did not exceed 3.8 per 100 thousand children aged 0–17 years, with this number varying from 1.2 to 2.1 among permanent residents. The risk indicators of primary infection among children aged 1–7 according to the Mantoux test (0.37% in 2019, 0.47%, in 2020, and 0.35% in 2021) and the prevalence of latent tuberculosis according to the results of screening based on RTA among children aged 8–17 in 2019–2021 (no more than 0.3%) indicate a stable epidemiological situation as regards tuberculosis infection in the city.
Conclusions. The development of an effective monitoring system for preventive tuberculosis screening among urban pediatric populations contributed to the detection of latent tuberculosis cases prior to the development of its local forms. The subsequent implementation of preventive measures in risk groups allowed the incidence of tuberculosis among children to be reduced.
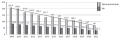
Aim. To estimate the geographical specifics of thyroid cancer (TC) morbidity and mortality among residents of the Far Eastern Federal District of Russia (FEFD) in 2008–2020.
Materials and methods. Data on TC morbidity and mortality provided by official statistical records, regulatory documents, as well as observations of TC dynamics were used.
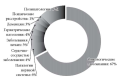
Results. In 2020, 548 new cases of malignant neoplasms of the thyroid gland were registered in the FEFD, which was 84% higher than in 2008 (298 people). The majority of the patients belonged to the age group of 40–60 years old. The number of patients with stages I–II increased (84.1%) under a simultaneous decrease in the number of patients with neglected forms of the disease (15.5%). The share of TC detected during preventive examination comprised 35.9% as compared to 16.0% in 2008. One-year mortality decreased to 3.3% as compared to 7.3% in 2008. At the same time, mortality rates remained at relatively high levels in the context of current achievements in oncology treatment. Morphological confirmation of the diagnosis was carried out in 98.7% of cases, which exceeded slightly the state level of 98.5%. The share of patients diagnosed five or more years ago comprised 66.8%, thus being lower that the national average value of 69.4%. The quality of oncology services was assessed using the index of registration reliability, which did not exceed 0.11 in any of the FEFD regions in the reporting year.
Conclusions. The observed increase in the number of patients with malignant neoplasms in the FEFD in 2008–2020 was accompanied by an increase in the annual incidence of thyroid cancer among both male and female populations, with the mortality levels demonstrating differences in the dynamics (increase/decline in men: – 50%; in women: + 29%).
Aim. To study the nutrient and energy intake of modern university students.
Materials and methods. 244 students aged 18–23 enrolled in specialist degree programmes were surveyed using a 24-hour dietary recall method adapted for online Google form surveying. The food intake was analysed based on the following aspects: meal frequency, intervals between meals and energy intake.
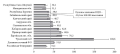
Results. According to the obtained results, 38.93 ± 3.12% of the respondents follow a 3–4 meal-a-day diet, with 3 main meals (breakfast, lunch and dinner) adhered by 71.31 ± 2.9% of students. In comparison with male respondents, female students were found to be more likely to keep main meals (74.87 ± 3.17% versus 59.65 ± 6.50%, χ2 = 4.94, p = 0.027). Additional meals (second breakfast, afternoon tea, overnight snack) were observed in 64.75 ± 3.06% of the students, with this share being significantly larger among male students (78.95 ± 5.40% versus 60.43 ± 3.58%, χ2 = 6.56, p = 0.011). About 68.44 ± 2.98% of the respondents reported long intervals between meals, which was found to be more typical of female students (71.66 ± 3.30% versus 56.14 ± 6.57%, χ2 = 4.84, p = 0.028). The energy intake of young people was established to correspond to the recommended norm in 27.40 ± 3.69% of cases.
Conclusions. The findings emphasize the importance of developing healthy eating habits in modern students, which can contribute to improving their health and increasing their educational performance.
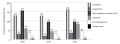
Aim. To study the parameters of 24-hour blood pressure monitoring in patients with polycythemia vera and to determine their informational value for the diagnosis of heart damage.
Materials and methods. Blood pressure parameters were monitored daily in 63 patients with I–IIB stage polycythemia vera and 52 healthy individuals to determine the occurrence of their pathological types. The sensitivity and specificity of the studied parameters were evaluated using ROC analysis for early diagnosis of heart damage in polycythemia patients. The obtained information was processed in Statistica 25.0.
Results. An analysis of blood pressure load showed that 47.6%, 30.1% and 34.9% of polycythemia patients suffer from systolic arterial hypertension (p = 0.012), daytime diastolic arterial hypertension (p = 0.03), and nocturnal diastolic arterial hypertension (p = 0.001), respectively. In comparison with healthy individuals, polycythemia patients experienced a higher variability of systolic (p<0.002) and diastolic (p<0.001) blood pressure, as well as the morning surge of systolic pressure (p = 0.014), more frequently. In 69.8% of polycythemia patients, pathological types of 24-hour blood pressure profile – with either insufficient or excessive nocturnal reduction – were observed. Informative parameters of heart damage in polycythemia patients were found to include blood pressure load, minimum daytime systolic and diastolic blood pressure, and the rate of nocturnal decrease in diastolic pressure.
Conclusions. (1) Systolic-diastolic arterial hypertension was detected in half of polycythemia patients, with pathological types of 24-hour blood pressure profile observed in the majority of patients. (2) The parameters of 24-hour blood pressure monitoring can be used for early diagnosis of heart damage in patients with polycythemia vera.
PRACTICE OBSERVATIONS
Publications in modern literature on tuberculosis and SARS-CoV-2 coinfection in children and adolescents are rare and insufficient. In this paper, we describe a clinical case of tuberculosis and SARS-CoV-2 coinfection in an adolescent child. An uncomplicated course of both diseases was demonstrated.
This paper presents a clinical case of a favorable tuberculosis chemotherapy outcome in a premature newborn. The role of early diagnosis in the development and outcome of the disease is shown. The newborn had no specific symptoms and clinical signs of tuberculosis. Therefore, when signs of an infectious disease appear in newborns, account should be taken of the mother’s medical history and the results of her fluorographic examination after childbirth. A favorable outcome can be achieved by timely separation of newborns from infected mothers, prompt commencement of specific chemotherapy, and patient management by phthisiatricians, neonatologists, and resuscitators.
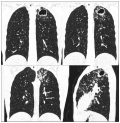
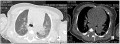
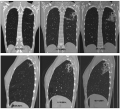
This paper presents a clinical case of destructive pulmonary tuberculosis in a child with drug resistance successfully treated using endoscopic bronchial valve therapy. In the context of the developed drug resistance to the causative agent of tuberculosis, ineffectiveness of the conducted treatment and negative radiological dynamics, the method of endoscopic bronchial valve treatment allows the patient’s condition and their clinical and radiological indicators to be improved. In the presented case, a positive X-ray dynamic was achieved in the form of closure of the decay cavity after the installation of an endobronchial valve. Following nine months, the installed endobronchial valve was removed during bronchoscopy and the continuation of chemotherapy was recommended.
PUBLIC HEALTH ORGANIZATION
The outpatient surgical care provided during the 2019–2021 COVID-19 pandemics was analyzed. In 2020, its volume was found to decrease, with the in-hospital stay of patients being reduced. As a result, the provision of such care to regional patients and the number of operations for malignant eyelid formations in Vladivostok Polyclinic No. 3 increased significantly.
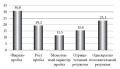
The efficiency of outreach diagnostics was assessed in 273 patients suffering from various forms glaucoma aged from 27 to 80 years. Following the developed algorithm, a set of instrumental and diagnostic tests was carried out to select 153 patients for surgical treatment and 64 patients for laser treatment. Necessary adjustments were made to the regimens of antihypertensive treatment for most patients, and recommendations were given. All glaucoma patients selected for surgical and laser treatment received timely and qualified assistance from specialists of the Khabarovsk branch of S. Fyodorov Eye Microsurgery Federal State Institution, which allowed the course of the disease to be stabilized and visual functions to be preserved. As a result, outreach consultations for patients with various forms of glaucoma showed their high efficiency. More than 60% of the examined patients were referred for surgical and laser treatment, 20% of patients were offered a corrected hypotensive regimen. Along with examining patients, outreach consultations provide methodological assistance for local ophthalmologists concerning the development of professional competencies in managing such patients. Due to a lack of ophthalmological services in regional polyclinical departments, the organization of outreach consultations for glaucoma patients is justified in terms of reducing cases of glaucoma progression and loss of visual functions.
Aim. To define the objectives of phthisiatric service with respect to organizing screening for tuberculosis infection (TB) and early diagnostics among adolescents in Primorsky Krai.
Material and Methods. The data of epidemiological monitoring conducted by the Primorsky Regional TB Dispensary in 1994–2021 were analyzed. The TB incidence, clinical structure of newly-diagnosed cases, phases of the tuberculosis process, as well as the presence of bacterial excretion were assessed. At a level of 0.95, the statistical hypothesis of equal shares was tested under an alternative hypothesis.
Results. The implementation of mass immunodiagnostics using the recombinant tuberculosis allergen (TBA) by medical organizations, which are joint into a unified medical network, improves screening efficiency of TB among adolescents. This is confirmed by a decreased TB incidence rate and improved clinical structure of newly-diagnosed cases. The prevalence of secondary TB forms in the clinical structure of newly-diagnosed cases in adolescents justifies the importance of annual fluorographic examination. Annual RTA testing and fluorographic examination of the chest in adolescents once every six months should be a priority anti-tuberculosis measure.
Conclusions. TB in adolescents remains to be a serious phthisiological problem. An effective system of screening and early detection of TB in adolescents should include mass immunodiagnostics and, with an interval of six months, fluorographic examination of the chest.
PEDAGOGY
A review study of interactive educational technologies as part of the educational process and their role in the clinical training of future pediatricians was carried out. The research was focused on the use of interactive technologies (on the example of role play) in teaching pediatrics students to ensure the formation of their professional competencies. Role play is a situational or demonstration technique applied to develop practical and communicative skills. This technique can be used to transform knowledge into skills most effectively by simulating real experiences that may arise in professional practice. Such simulationbased learning allows trainees to experience some concept or idea by acting it out in front of peer students, or by watching others. Role play is useful for developing communicative and decision-making skills. The effectiveness of interactive teaching methods is determined by the joint activity of the teacher and the students. In this context, education is seen as the formation of new goals and personal attitudes, while personal development is seen as the formation of personal capacity for independent activity and self-management.